
Occupational Health and Safety Management — Mental Health and Safety at Work
What is ISO 45003:2021?
This standard provides organizations with guidelines for managing psychosocial risks, enabling them to help prevent work-related employee injuries and health issues and promote workplace well-being.
The benefits of organizational certification

01. Demonstrate a commitment to employee health
Obtaining ISO 45003 certification demonstrates your organization's commitment to employee well-being, signaling to current and potential talent that your organization provides a healthy and supportive work environment. The benefits of this certification are realized by everyone—both your employees and your organization.

02. Enhance workplace productivity and engagement
ISO 45003 certification focuses on managing and minimizing workplace stressors to prevent negative human capital outcomes. By minimizing these stressors, organizations can achieve higher levels of productivity, engagement, retention, and reduced absenteeism.

03. Empower your organization with purpose
Every organization has its unique employee risk factors. By implementing continuous improvement processes, considering risks, measuring stress levels, and assessing employee outcomes, the organization demonstrates its commitment to workplace health.

04. Proudly display your organization's badge
Your commitment to HR excellence and employee experience is significant. That’s why certified organizations are provided with digital badges, based on global standards, which validate your company as an outstanding workplace. These badges showcase your culture and commitment to excellence and serve as a powerful recognition tool that helps attract top talent, retain high performers, and enhance your reputation in the talent market.
Even with limited resources, there is still a lot that can be done.
When the HR department has done everything it can, what else can you do? ISO 45003, the first... gives you the answer!
This is the core idea of ISO 45003, the world's first occupational health and safety management standard—'Psychological health and safety at work — Guidelines for managing psychosocial risks.'
In today's fast-paced work environment,
ensuring employee well-being is more important than ever.
Our work life has a significant impact on our mental health,
Employers have a responsibility to protect the physical and psychosocial health of their employees.
The values and principles behind ISO 45003
| A people-centered preventive approach can be succinctly expressed as follows: | |
|---|---|
| Vision | Build a world of trust |
| Mission | Starting from your organization's CEO and top management |
| Goals | Respect employees by providing good compensation, benefits, and a healthy work-life balance. Empower people and build a supportive system both within and outside your organization. |

Does this topic need to be on the agenda?

Committee members
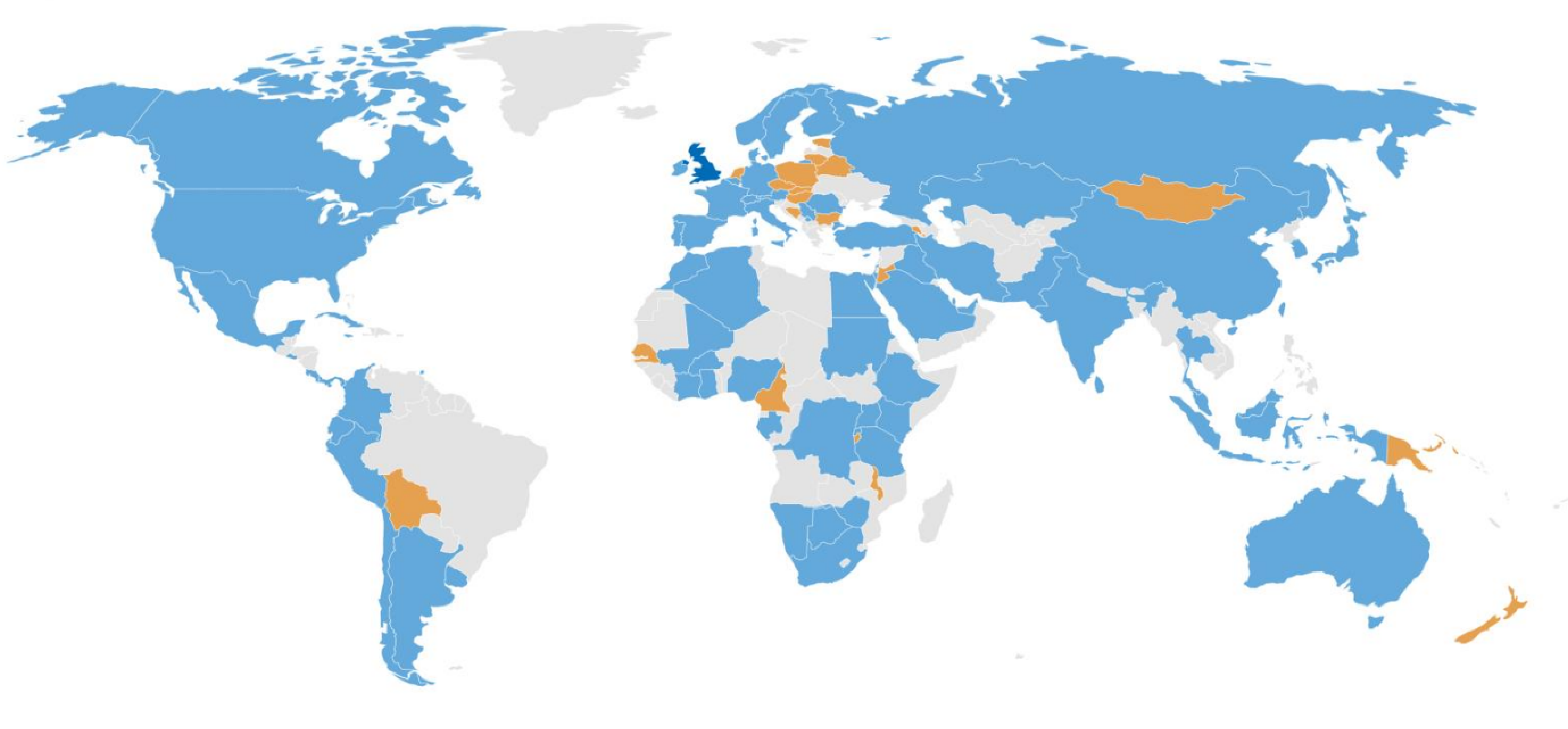
The World Health Organization (WHO) Healthy Workplace Model

How does ISO 45003 help organizations?
We offer training, gap assessments, and certification audits to support your journey toward ISO 45003 compliance.

- Encourages employees to be more proactive and motivated
- Supports recruitment, attracts talent, retains employees, and promotes workforce diversity
- Enhances employee engagement
- Fosters innovation
- Ensures compliance with regulations
- Reduces absenteeism, inefficiency, and even disruption caused by workplace stress, burnout, anxiety, and depression
If your organization wishes to
Address the following issues:
- How psychological harm occurs in the workplace?
- What is psychosocial health and psychosocial risks?

- Eliminate and address low risks
- Practical case studies for addressing issues
- Efforts made but results are unsatisfactory
- Best practices and frameworks are needed to improve

- I tried hard, but the results were not good
- Best practices and frameworks are needed to improve













What are the specific steps to obtain certification?
- Determine whether the organization meets the requirements of ISO 45003.
- Evaluate the organization’s current occupational health and safety management practices regarding psychological health and safety to ensure that the management of psychosocial risks meets the standard's requirements.
- Develop or update relevant policies, objectives, plans, and procedures.
- Ensure that all employees are aware of and engaged with the management system.
- Implement psychological health and safety measures within the occupational health and safety management system: manage psychosocial risk management plans and monitor their effectiveness.
- Provide training to employees to enhance awareness of psychological health and safety.
- Conduct regular internal audits to assess the effectiveness of the management system.
- Management must regularly review the management system to ensure it remains appropriate, adequate, and effective.
- Conduct a formal third-party audit to verify that the organization meets all the requirements of the ISO 45003 standard.
- Third-party audits are typically conducted by certification bodies, which must be accredited by a recognized accreditation body.
- Based on the results of the third-party audit, take necessary corrective and preventive actions.
- Once the audit is successfully completed, the organization will be awarded the ISO 45003 certification.
- After certification, annual surveillance audits are required to ensure ongoing compliance with the standard's requirements over the two-year certification period.
- After obtaining certification, the organization should continue to monitor and improve the management system to address new risks and challenges.
- Each step needs to be carefully executed to ensure that the management system operates effectively and complies with the requirements of the ISO 45003 standard.
- Additionally, organizations should always stay informed about the latest standards and regulations, and update their management systems as needed to respond to any changes.
What is legal certification?
What are the consequences of obtaining certification from a 'certification body' that does not have the qualifications stipulated by the 'Regulations on Certification and Accreditation of the People's Republic of China'?
- Invalid Certification: Certification certificates issued by unqualified certification bodies do not have legal validity and cannot serve as proof of product quality, service level, or other relevant standards.
- Legal liabilities: If a company promotes or misleads consumers using invalid certification certificates, it may be deemed false advertising. Under laws such as the "Anti-Unfair Competition Law of the People's Republic of China," it could face administrative penalties, including fines and orders to cease illegal activities. If it's a publicly listed company, it may also mislead investors due to "business fraud," resulting in collective lawsuits and claims from investors.
- Loss of credibility: Consumers and partners may lose trust in a business due to its dishonest behavior, resulting in damage to the company's reputation.
- Economic loss: A company may lose market opportunities due to using invalid certifications or incur fines from illegal activities, resulting in financial losses.
- Breach of contract: If a contract explicitly requires products or services to have valid certifications, using invalid certifications may result in a breach of contract.
- Market access restrictions: Certain markets or industries have strict certification requirements, and products or services without valid certifications may be unable to enter the market.
For publicly listed companies, what serious consequences may arise from obtaining certification from a "certification body" that does not have qualifications specified in the "Regulations on Certification and Accreditation of the People's Republic of China"?
- Information disclosure violations: Publicly listed companies are obligated to disclose truthful, accurate, and complete information to the public and regulatory authorities. If a company includes invalid certification information in its disclosures, it may be considered a violation of information disclosure requirements.
- Securities fraud: If a publicly listed company intentionally uses invalid certifications to mislead investors, it may be deemed securities fraud, which could result in severe penalties under the "Securities Law of the People's Republic of China" and other relevant regulations.
- Stock price volatility: Once the use of invalid certifications is exposed, it may trigger panic among investors, leading to a decline in the company's stock price, adversely affecting its market value and financing capabilities.
- Investor lawsuits: Misled investors may file collective lawsuits against the company, seeking compensation for losses incurred due to reliance on invalid certifications.
- Regulatory penalties: Securities regulatory authorities may investigate the company and impose appropriate measures based on the findings, such as warnings, fines, orders for correction, or market bans.
- Internal management issues: The use of invalid certifications may lead to internal reviews, raising questions about the management's competence and affecting the company's internal management and decision-making.
- Criminal liability: In extreme cases, if the company's actions constitute a crime, relevant responsible parties may face criminal charges.
What are the legal consequences of using illegal certification?
If a company uses a certification issued by a body not accredited by the Certification and Accreditation Administration of the People's Republic of China (CNCA), it may face the following legal consequences:
Administrative Penalties
If a company uses certifications issued by organizations not accredited by the Certification and Accreditation Administration of the People's Republic of China (CNCA), market regulatory authorities will impose penalties for the act of falsifying or misusing certification marks.
Civil Liability
If a company's fraudulent certification activities cause losses to other organizations, it will be required to bear corresponding civil liability for compensation.
Criminal Liability
If a company's actions constitute a crime, such as counterfeiting or altering certification certificates or marks, it will be subject to criminal liability.
Market Ban
Companies with severe violations may be banned from entering the relevant market or industry for a specified period or permanently.
Supervision and Inspection
Companies will undergo stricter supervision and inspection by market regulatory authorities to ensure the legality of their business activities.
How to determine if a company's certification is legitimate?

How to verify if a certification body has legitimate qualifications?


About the International Organization for Standardization
 The International Organization for Standardization (ISO), established in 1947, is an international organization in the field of standardization. It defines itself as a non-governmental organization with English, French, and Russian as its official languages. ISO has 165 members, including national standards bodies from member countries and major industrial and service enterprises. The Standardization Administration of China (under the State Administration for Market Regulation) joined ISO in 1978. In October 2008, at the 31st ISO General Assembly, China officially became a permanent member of ISO. ISO is responsible for standardization activities across most sectors worldwide, conducting technical work through 2,856 technical structures (including 611 technical committees, 2,022 working groups, and 38 special working groups).
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO), established in 1947, is an international organization in the field of standardization. It defines itself as a non-governmental organization with English, French, and Russian as its official languages. ISO has 165 members, including national standards bodies from member countries and major industrial and service enterprises. The Standardization Administration of China (under the State Administration for Market Regulation) joined ISO in 1978. In October 2008, at the 31st ISO General Assembly, China officially became a permanent member of ISO. ISO is responsible for standardization activities across most sectors worldwide, conducting technical work through 2,856 technical structures (including 611 technical committees, 2,022 working groups, and 38 special working groups).
Official introduction to ISO 45003:2021 certification https://www.iso.org/standard/64283.html